How a Secure Enclave Solves BYOD Challenges

As Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) becomes more prevalent, the need for robust security measures grows. BYOD empowers employees with flexibility and choice, but it poses unique challenges for IT and security teams.
When employees have direct access to sensitive data from their personal devices, IT teams need a way to protect data while also respecting user privacy. A Secure Enclave is the solution to this challenge.
What Is a Secure Enclave?
A Secure Enclave is a separate, secure trusted execution environment on a device. This technology has been a feature in Apple devices since 2014, protecting sensitive data like Touch ID and Face ID. Today, the Secure Enclave is the best solution for BYOD environments, because it isolates work-related and personal activities to prevent cross-access.
Within the secure enclave, data and applications are encrypted and completely isolated from the rest of the device, maintaining end-user privacy.
The Challenges of Managing BYOD
Historically, organizations have tried to manage BYOD environments with various types of security solutions — VDI, VPN, and DaaS, for example. However, that technology was complex to configure, didn’t guarantee user privacy, and frustrated end users with latency.
Secure Enclaves provide a trusted execution environment, ensure a limited attack surface, and protect user biometric data and personal details.
Secure Enclave Features and Capabilities
Here are seven Secure Enclave features that set it apart from the “old” ways of managing BYOD:
1. Isolation and Protection
A Secure Enclave sits on the personal device, and everything within is company-managed, but personal activities are off-limits to the organization. The Secure Enclave has a distinct border so users can see both personal and business applications and activities.
This separation ensures that personal files and activities remain private, and work data is fully protected from zero-day vulnerabilities, privilege escalation attacks, and other risks.
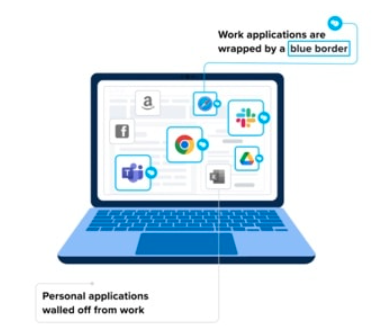
Venn’s Blue Border feature denotes which applications are work-related.
2. Data Security
A Secure Enclave includes an encrypted, unwritable virtual drive accessible only to applications and data within the enclave. Organizations can manage permissions, enforce access policies, and enable multi-factor authentication within the secure enclave.
For data at rest, the Secure Enclave ensures FTC Safeguards compliance with features like DLP controls, including limitations on file access, storage, browser usage, copy/paste, screen capture privileges, and peripheral usage.
For data in transit, all network traffic within the Secure Enclave is routed through a secure tunnel, via a static, dedicated IP unique to the company. This process is supported by protocols like HTTPS and TLS, and data is inaccessible to users who don’t have the proper encryption keys. Encrypted data is protected, should malware infect parts of the device outside the Secure Enclave.
3. Localization
Work-related applications launch locally on the unmanaged device within the Secure Enclave. This minimizes latency and provides a native application experience, which is often more user-friendly than virtual desktop environments.
4. Simplified Onboarding and Offboarding
Businesses can deploy a Secure Enclave quickly via a welcome email to new employees that includes a link for downloading essential applications and accessing their secure environment. When an employee leaves a company, administrators can remotely wipe all work-related data in the Secure Enclave without affecting personal files.
5. Device-Agnostic Usage
Similarly to how MDM technology works for iOS devices and Android devices, a Secure Enclave supports any personal laptop – Mac or PC. Employees appreciate this flexibility, and they’re most productive using their preferred device and operating system.
6. User Privacy
Employers can’t access or monitor user activities outside the Secure Enclave, ensuring personal data, browsing history, and applications remain private and untouched. This allows users to feel comfortable using their devices for personal use.
7. Compliance
Because a Secure Enclave isolates and secures sensitive internal data and customer data, it helps companies ensure compliance with HIPAA, FINRA, SEC, NAIC, GDPR, and/or SOC 2 requirements. It safeguards electronic medical records and protected health information (PHI), and a Secure Enclave also makes it easy to document compliance.
Secure Enclave Advantages vs. Traditional Security Measures
Is a Secure Enclave really superior to traditional security measures for BYOD? Yes. Read how it stacks up against the alternatives for nine key attributes:
1. Secure Enclave vs VDI – Application Performance
Unlike a cloud-hosted or centralized VDI, Secure Enclaves prevent dependence on constant internet connectivity and the costs and complexities of maintaining server-based application delivery.
2. Secure Enclave vs VDI and DaaS – Attack Surface
The security of VDI and DaaS platforms is highly dependent on end users updating their devices. If employees don’t install operating system updates or security patches, their employer’s task surface expands.
With a Secure Enclave, businesses can protect network data and files, regardless of the end user’s security measures. The separation of personal use and a trusted execution environment minimizes BYOD security risks for businesses.
3. Secure Enclave vs VPNS & Air-Gapped Systems – Network Isolation
A Secure Enclave protects work-related data by routing traffic through secure, private company gateways, and personal applications and internet activity outside the enclave operate as usual. VPNs or air-gapped systems impose complete network segregation and are more complex to manage.
4. Secure Enclave vs EDR – Logging and Monitoring Tools
With a Secure Enclave, remote monitoring occurs only within the secure environment. Other BYOD technology — the EDR, for example — monitors the user’s entire device and tracks network access. This process can protect sensitive data, but it also creates privacy concerns for employees and may cause friction in the employer-employee relationship.
5. Secure Enclave vs EDR & EPP – Endpoint Security Solution
While a Secure Enclave provides strong protection for data and applications within its workspace, it’s not a replacement for traditional endpoint security tools such as antivirus software, EDR, or EPP. Those tools protect the entire device from threats like malware, phishing, and unauthorized access. A Secure Enclave focuses solely on isolating and securing the company-managed environment without extending its protection to the rest of the device.
6. Secure Enclave vs IAM & ZTNA – Access Management
A Secure Enclave isn’t an identity or access management (IAM) solution. While it can enforce access policies within the enclave, its core capability is not verifying BYOD users for network access, like a ZTNA solution. Integrating Secure Enclaves with existing IAM solutions ensures access control extends beyond the enclave to all enterprise resources, maintaining a comprehensive security framework.
7. Secure Enclave vs VDI – Permissions Controls
With VDI, admins can’t control which apps and tools are installed on a user’s personal device. A Secure Enclave lets admins control which tools and apps are available to end users in the enclave. Admins can restrict or disable browser plugins and disable password autofill, and all policy settings are stored securely in the cloud, where end users can’t modify them.
A Secure Enclave also prevents the end user from storing encrypted data, copy/pasting Secure Enclave data onto their device, or capturing screenshots within the enclave.
8. Secure Enclave vs Enterprise Browsers – Protection Coverage
Web-based BYOD platforms like Enterprise Browsers only secure browser-based activities or web applications. A Secure Enclave safeguards both web and local applications for work, including all files, data, and activity within the enclave.
9. Secure Enclave vs VDI – User Experience
VDI technology helped businesses manage remote devices when remote work wasn’t as prevalent, but it hasn’t evolved to meet the needs of today’s BYOD environments. Even when the user works from their secure device, none of their activity is local — every action occurs remotely in the VDI trusted execution environment. That means tasks like video conferencing or working on large files can be disrupted by latency and jitter.
A Secure Enclave processor is designed to handle the demands of digital workplaces. It removes frustrating latency bottlenecks and boosts productivity. And because it reduces tedious IT tasks and ensures privacy for end users, a Secure Enclave helps businesses build better relationships with employees and contractors.
Venn: The Secure Enclave for Enterprise BYOD Environments
Are you ready for a better way to manage BYOD? Join the 700+ organizations that trust Venn to ensure compliance, enhance security, and enable the best user experience for employees.
Discover how Venn’s patented Blue Border technology offers unparalleled flexibility and security. Request a product demo today.
More Blogs


